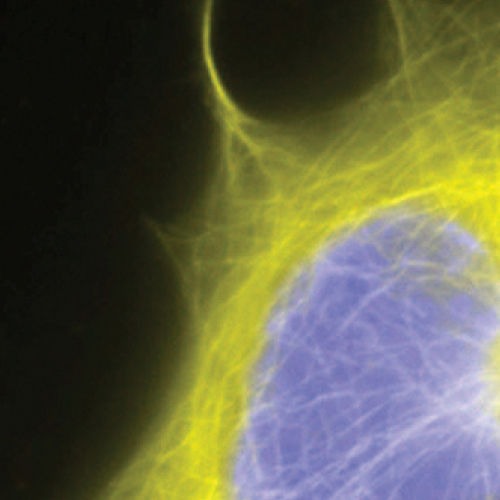
Cell Imaging
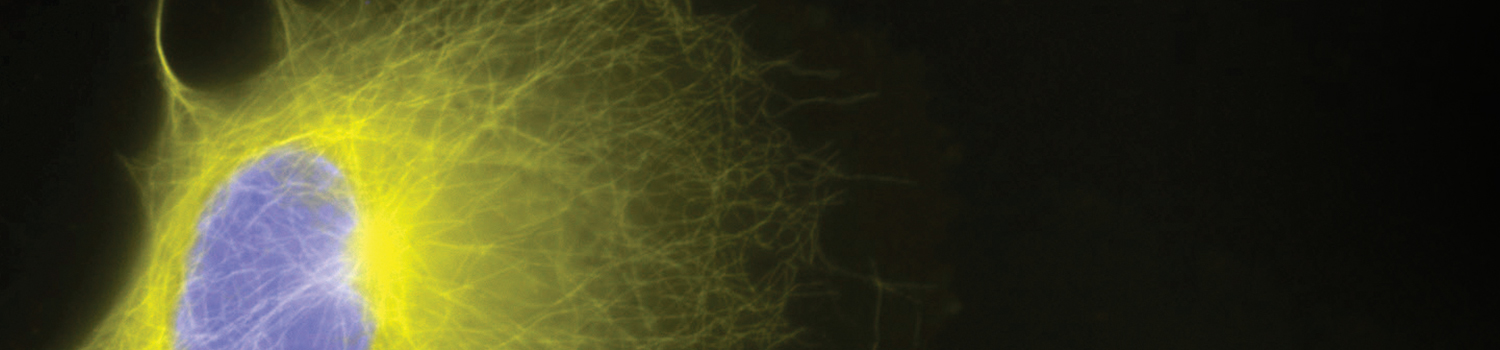
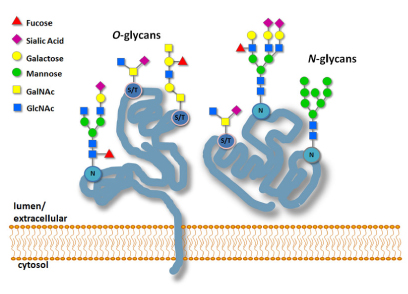
Cell imaging analysis can use fluorescent dyes, fluorophore labeled molecules or recombinant protein plasmid systems. Recombinant protein labeling systems and bioluminescent reporter systems are among the most sensitive fluorescence methods for imaging ____expression____, transport, co-localization and degradation in either fixed or living cells. Protein labeling systems offer many advantages. For example, color changes can be easily implemented by using different substrates. Protein labeling systems can involve the use of tag-specific antibodies or antibodies to separate epitopes engineered into a plasmid tag system for detection. Protein labeling systems can be used with non-cell permeable substrates to enable the specific imaging of cell surface targets. This strategy is not possible with bioluminescent recombinant systems. In living cells, protein labeling substrates can be introduced and followed in cells over time. Two separate cellular targets can also be imaged simultaneously, using protein labeling systems with mutually exclusive, tag specific fluorescent substrates. Cellular functions and structures can be visually detected using methods such as wide-field fluorescence, confocal, time-resolved and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy, or cell based high content assays. Given cellular target characteristics and the array of possible detection methods, choosing an optimal fluorescence system for cellular imaging is key to experimental design.
Feature
- 1
Clone and express once, then use with a variety of substrates
- 2
Non-toxic to living cells
- 3
Wide selection of fluorescent substrates
- 4
Highly specific covalent labeling
- 5
Simultaneous dual labeling
Specification
CLIP Surface
SNAP Cell
SNAP Surface
SNAP Companion
CLIP Cell
Product Information
Cell Imaging
| Cat No. | SIze | |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-SNAP-tag® Antibody (Polyclonal) | P9310S | 100 µl |
| BC-NH2 | S9236S | 2 mg |
| BG-GLA-NHS | S9151S | 2 mg |
| BG-Maleimide | S9153S | 2 mg |
| BG-NH2 | S9148S | 2 mg |
| BG-PEG-NH2 | S9150S | 2 mg |
| CLIP-Surface™ 488 | S9232S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Capture Magnetic Beads | S9145S | 2 ml |
| SNAP-Capture Pull-Down Resin | S9144S | 2 ml |
| CLIP Surface | ||
| CLIP-Cell™ 505 | S9217S | 50 nmol |
| CLIP-Cell™ Block | S9220S | 100 nmol |
| CLIP-Cell™ TMR-Star | S9219S | 30 nmol |
| CLIP-Surface™ 547 | S9233S | 50 nmol |
| CLIP-Surface™ 647 | S9234S | 50 nmol |
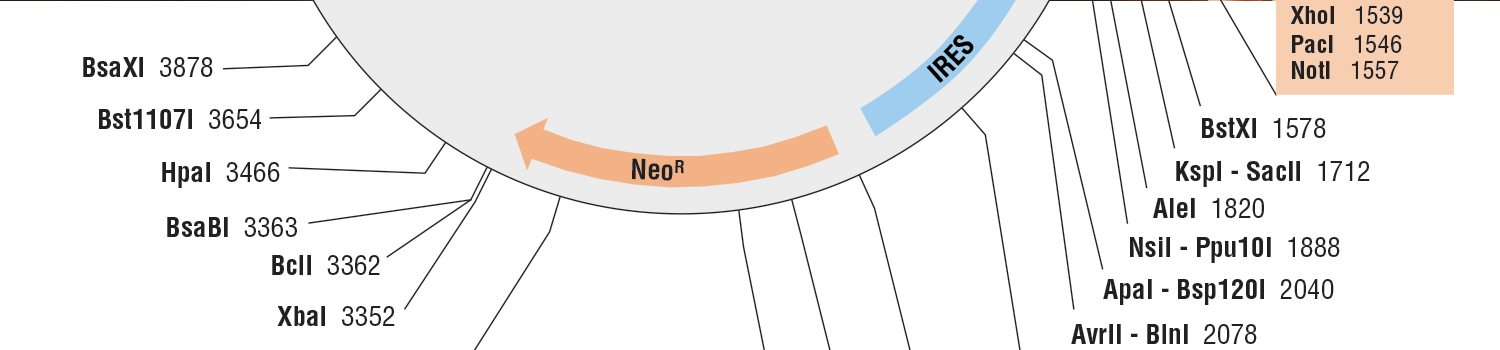
| pCLIPf Vector | N9215S | 20 µg |
| SNAP Cell | ||
| SNAP-Biotin® | S9110S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Cell® 505-Star | S9103S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Cell® Block | S9106S | 100 nmol |
| SNAP-Cell® TMR-Star | S9105S | 30 nmol |
| SNAP-Cell® 430 | S9109S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Cell® 647-SiR | S9102S | 30 nmol |
| SNAP Surface | ||
| pSNAPf Vector | N9183S | 20 µg |
| pSNAP-tag® (T7)-2 Vector | N9181S | 20 µg |
| SNAP-Surface® 488 | S9124S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Surface® 549 | S9112S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Surface® 594 | S9134S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Surface® 649 | S9594S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Surface® Alexa Fluor® 488 | S9129S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Surface® Alexa Fluor® 546 | S9132S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Surface® Alexa Fluor® 647 | S9136S | 50 nmol |
| SNAP-Surface® Block | S9143S | 200 nmol |
| SNAP Companion | ||
| Anti-SNAP-tag® Antibody (Polyclonal) | P9310S | 100 µl |
| SNAP-tag® Purified Protein | P9312S | 50 µg |
| CLIP Cell | ||
| CLIP-Biotin | S9221S | 50 nmol |
| CLIP-Cell™ 505 | S9217S | 50 nmol |
| CLIP-Cell™ Block | S9220S | 100 nmol |
| CLIP-Cell™ TMR-Star | S9219S | 30 nmol |
| pCLIPf Vector | N9215S | 20 µg |